What Factors Affect the Luminous Efficiency of a LED High Bay Light
What Factors Affect the Luminous Efficiency of a LED High Bay Light
LEDs are more and more widely used due to it is much energy-saving and environmental friendly. And high luminous efficiency LED lights are more and more popular as it means higher efficiency when transforming electricity to light and saving more energy. But do you know what factors affect the luminous efficiency of an LED light fixture?
There are three main factors that affect the luminous efficiency of a finished LED light fixture directly——the luminous efficiency of LEDs, the light transmittance of lens, and the efficiency of the driver. Let’s check these factors separately.
1. Luminous efficiency of the LEDs
The light comes from a semiconductor P-N junction, and the luminous output increasing together with the working current. While more current creates more heat and makes the luminous efficiency decreased with current increasing(LED junction temperature rising when current increased). Below is a typical luminous output diagram of Lumileds Luxeon 3030 2D LEDs:
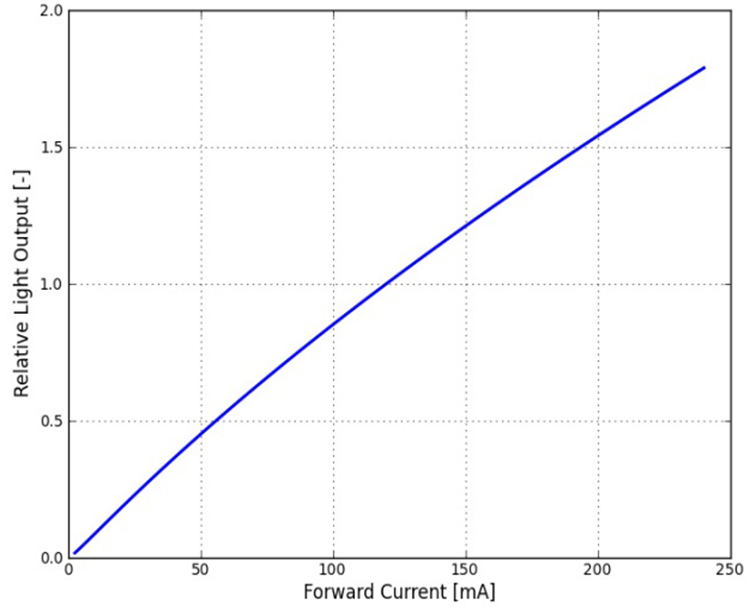
Figure 1. Typical normalized light output vs. forward current
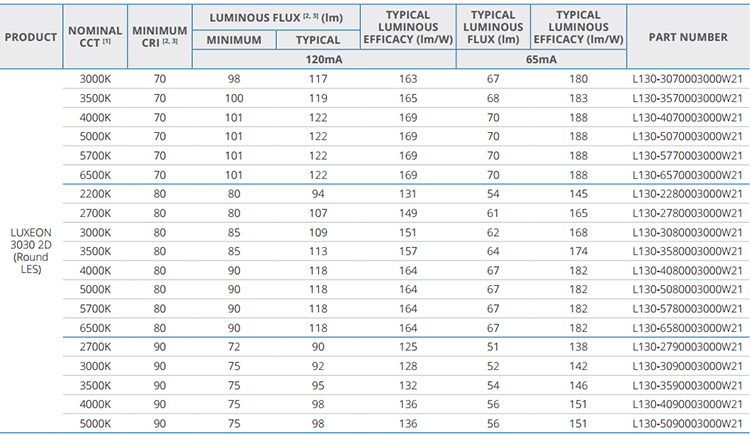
Figure 2. Product performance of LUXEON 3030 2D at 120mA and 65mA at specified temperature
We can see luminous output increased, while luminous efficiency decreased with current increasing.
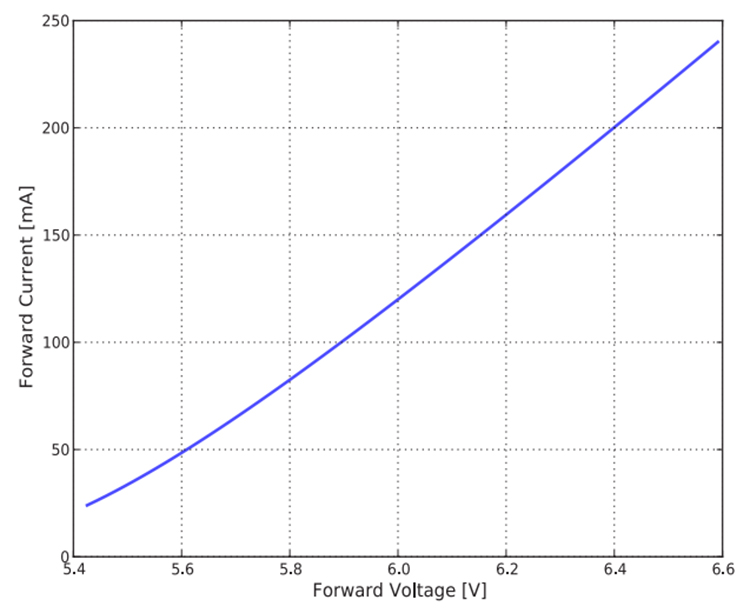
Figure 3. Typical forward current vs. forward voltage
2. Light Transmittance of Lens
When light passes through the glass, some of the light will be absorbed and reflected at the same time. The light transmittance of the glass determines how many percent light can pass through the glass.
3. LED Driver Efficiency
As we know the driver itself consumes some of the power when it works. The driver efficiency determines how many percent of the power left and can be used on the LEDs. So higher driver efficiency means less waste of power, and surely affect the luminous efficiency of a lamp. Below is the efficiency vs load diagram of the Meanwell HBG-240 series driver.
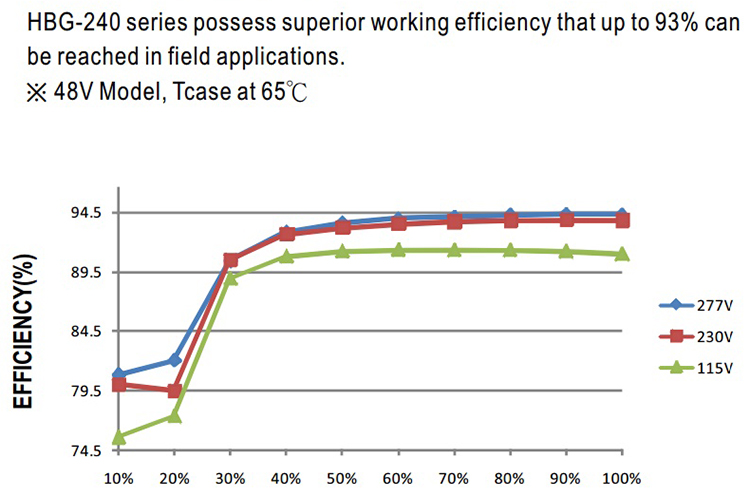
Figure 4. Efficiency vs. Load
Let’s see a 200 watts UFO LED high bay light as an example.
Logos Lighting’s UFO LED high bay light is packed with Meanwell driver and Lumileds or Osram LEDs. The driver efficiency of Meanwell HBG-240 series drivers is 93%. This means there are 200*93%=186 watts power will work on the LEDs. Considering for 200W light fixture with 315pcs LEDs, the power is 186/315=0.59W per LED when working. According to figure 3, we know that the current is about 100mA at 0.59W per LED. In the meantime according to the above 3 figures, we can also calculate the luminous efficacy of LEDs is about 175lm/w at 100mA(70Ra, 5000K). Considering light transmittance 95% of the lens, the luminous efficiency of 200W LED high bay fixture is 175*93%*95%=154.6lm/w on an approximate calculation.
We can calculate the luminous efficiency of other lights with the same method, only need to know a few factors of some main accessories used for the lighting fixtures.
If you have any questions or suggestions, please feel free to contact us.
(Note: Figures 1, 2, 3 are according to the specification of Lumileds Luxeon 3030 2D LEDs, and figure 4 are according to the specification of Meanwell HBG-240 drivers.)

